Responsive Web Design
Responsive Overview
Responsive web design is the practice of building a website suitable to work on every device and every screen size, no matter how large or small, mobile or desktop.
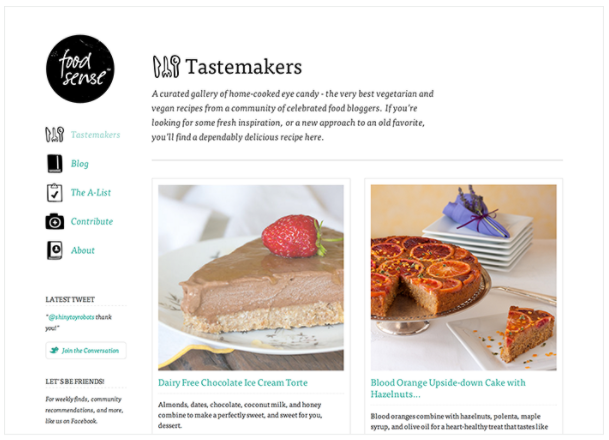
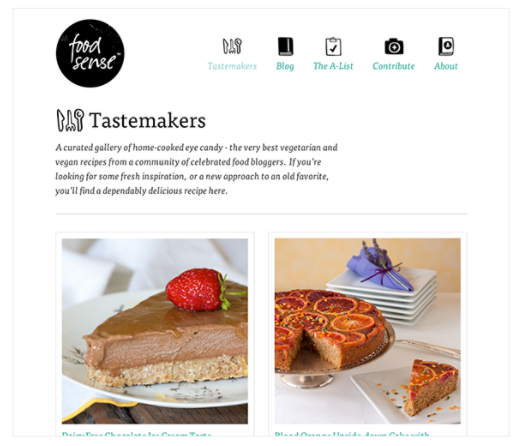
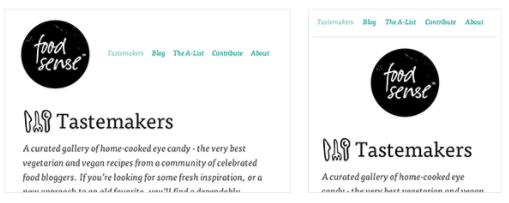
Flexible Layouts
Responsive web design is broken down into three main components, including:
- flexible layouts
- media queries
- flexible media
The first part, flexible layouts, is the practice of building the layout of a website with a flexible grid, capable of dynamically resizing to any width. Flexible grids are built using relative length units, most commonly percentages or em units. These relative lengths are then used to declare common grid property values such as width, margin, or padding.

The not logical operator negates the query, specifying any query but the one identified. In the example below the expression applies to any device that does not have a color screen. Black and white or monochrome screens would apply here for example.


Mobile First
Viewport





